A VARIETY of popular e-cigarette products have been found to contain dangerous bacterial and fungal toxins linked to serious health conditions like lung disease.
That’s according to an alarming new study from the Harvard School of Public Health.
They found impurities associated with conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive lung disease were present in nearly a quarter of all single-use e-cigarette cartridges.
These same impurities were also found in over three quarters of e-liquids tested.
“Finding these toxins in e-cigarette products adds to the growing concerns that we have about the safety of e-cigarettes,” Dr. David Christiani, study author and professor of environmental genetics at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public in Boston, said.
A total of 75 popular e-cigarette products - 37 single-use cartridges and 38 e-liquids – were studied as part of the research.
These products were divided into four different flavour categories: tobacco, menthol, fruit, and other; before being screened for the presence of endotoxin and glucan.
Endotoxin is a potent inflammatory molecule found in bacteria that can seriously damage the lungs.
Glucan is another toxic substance founds in the cell walls on most fungi.
Exposure to either of these microbial toxins has been associated with health problems like asthma, lung inflammation and reduced lung function.
According to the study, 17 of the 75 products contained traces of endotoxin, which amounts to around 23% of the total.
More alarmingly, however, is the fact that 61 of the 75 products tested contained traces of glucan – a figure that equates to around 81%,
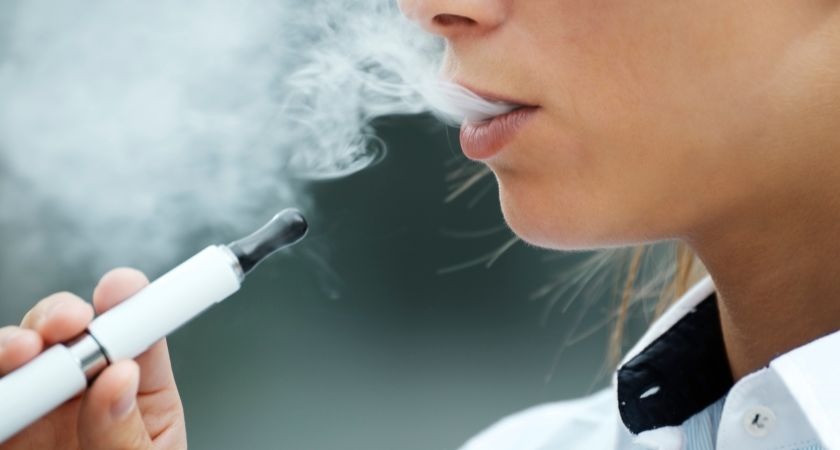

Endotoxin concentrations were found to be higher among fruit-flavoured products, suggesting the raw materials used in the production of these distinctive flavours could be the chief source of the contamination.
Despite these alarming findings, researchers were unable to confirm at what point in the production process contamination occurred.
One potential source could be the cotton wicks used in e-cigarette cartridges as both glucan and endotoxin are known contaminants of cotton fibres.
“In addition to inhaling harmful chemicals, e-cig users could also be exposed to biological contaminants like endotoxin and glucan,” Mi-Sun Lee, a Harvard research fellow and lead author of the paper said.
“These new findings should be considered when developing regulatory policies for e-cigarettes.”
Dr Christiani called for an increase to the public education offered on the potential health consequences of long term e-cigarette use.
“There needs to be much stronger regulation of the production and purity of the compounds used in e-cigarettes," he said. "People should not assume that e-cigarettes are safe."
The full study was published by Environmental Health Perspectives and can be accessed here.